Effects of third-party cookies in Canvas
On this page:
- Changes to Chrome
- If you suspect third-party cookies are causing an error
- Temporary fix for instructors
- More about cookies
Changes to Chrome
In February 2020, Google released version 80 of its Chrome web browser, which changes the way third-party cookies are handled. By default, Chrome will block third-party cookies unless the embedded web application takes necessary steps to prevent the cookies from being blocked.
In Canvas, you may experience difficulties launching third-party tools from the course navigation menu, course modules, and elsewhere while UITS works with application providers to patch their software to comply with Chrome 80.
If you suspect third-party cookies are causing an error
- Try a different web browser: This is often the quickest troubleshooting step to try. If you have another browser (or two), try opening the problematic page in a different web browser to see if it functions properly.
- Visit the embedded tool directly to establish "first party trust" with it: If you know the website URL for the embedded service that you suspect is failing due to a blocked third-party cookie, try visiting that website in its own browser tab. This may establish what's called "first party trust" with the external application, allowing the embedded application to then function properly in Canvas.
- Contact the Support Center: Your campus Support Center may be able to help you troubleshoot the issue and determine if third-party cookies are in fact the problem.
- Report the problem to your instructor: If you experience problems loading external tools in Canvas, alert your instructor. It may be possible to provide access to the external tool/resource in a way that does not involve third-party cookies.
Temporary fix for instructors
If a third-party tool is broken in your course site due to a third-party cookie issue, try this workaround:
- Create a new module in your course site called "Canvas Third-party Tools" or another name you choose. (If you aren't sure how to use Canvas Modules, see the Modules section of the Canvas Guides).
- In the new module, click (Add Item) to add a new item to the module.
- From the drop-down menu in the "Add Item" window, select .
- Select the desired tool from the external tools list. Scroll to the bottom of the window and check . Loading the tool in a new tab will circumvent the third-party cookies problem. If you wish, you can also change the display name of the tool by editing the Page Name.
- To finish adding the tool to the module, click .
- Repeat steps 1-5 for each problem tool.
- Publish the module and items. Your students will now be able to launch the tools from Canvas Modules.
If you receive an "Access Denied" message:
- Make sure you're running the most recent version of Chrome; to update your browser, see Update Google Chrome.
- In Chrome, visit chrome://flags.
- At the top of the page, in the "Show flags" box, type
samesite. - Next to "SameSite by default cookies", make sure the drop-down is set to .
More about cookies
How browsers use cookies
When a website needs to keep track of something about your interaction with the site (such as settings or preferences), it will often store a small text file called a cookie in your web browser's storage. Cookies allow websites to "remember" your settings in between browsing sessions, so that when you leave the site and come back later, the site will preserve your settings. This is a useful mechanism, and an extremely common part of how websites and web browsers work.
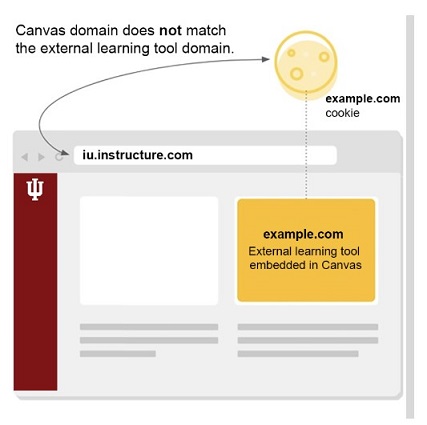
About third-party (or "cross-domain") cookies
Websites often embed external resources and experiences from other web materials served from another location on the web. Canvas, for example, may embed a learning tool inside a frame in the Canvas environment. These external web applications will sometimes need to store their own cookies. Since the external web application is being served from a different domain, or URL, than the one you see in the browser's URL bar, this cookie is considered to be third-party (or cross-domain).
How browsers handle third-party cookies
Since third-party cookies operate in a different domain than the main website that you may be visiting, some web browsers may block these cookies in some circumstances, depending on how the external application's cookies have been structured. Depending on how the third-party application is programmed, it may not function as expected, or it may fail to function entirely (with or without an error message). In short, the way an application behaves when the web browser blocks third-party cookies depends on the application's programming, and may vary.
This is document bdnr in the Knowledge Base.
Last modified on 2021-09-20 16:24:42.