Data Cookbook definition workflow cheat sheet
On this page:
About workflows
Workflow definition
In Data Cookbook, a workflow is a predefined process for approving an object or a request for information. Data Cookbook includes a customizable workflow engine. Custom workflows specific to Indiana University were created and tested for adoption by the IU Data Cookbook community during the first quarter of 2017.
Workflow types
Data Cookbook includes three basic workflow types: definition approval, specification approval, and information request resolution. At IU, Data Cookbook only uses workflow for definitions and specifications.
Workflow stages and steps
Stages
Each workflow has several stages that represent a point in the process that requires specified action from one or more users or groups of users.
Happy path
In Data Cookbook, "happy path" is a term that describes the most common approval process. In project management terminology, this would be the critical path. Steps with green-colored transition action buttons are the happy path for the stage.
Steps
In a stage, steps represent available tasks and/or groups of actions. Steps can be required or optional and may be assigned to specific users or user groups based on the workflow object's attributes.
Transition actions
Transition actions are associated with steps within stages and represent what a user does to move an object from one stage to another. These actions appear as buttons on the definition or specification. The transition actions available to a user will depend on both the user's role and the workflow stage that contains the object.
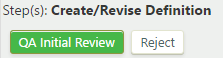
In the following example, two transition actions are available; you can send the definition to QA or reject it:
Conditions
Conditions function as "where" clauses for workflows. Conditions let you specify appropriate workflows or steps based on criteria such as functional area, data system, or classification code.
Workflow permissions
Workflow stages, steps, and transition actions are governed by permissions handled by interactions between user groups, assignment mappings, and named roles.
User groups
User groups are the primary means for granting permissions within Data Cookbook, especially in the absence of workflow integration. You can grant user groups permissions for definitions, specifications, and technical information based on functional area. For specifications and definitions, these permissions are manager, editor, and viewer. For technical information, these permissions are editor, view, and hidden. Any user assigned to the group will have the permissions associated with the group.
User groups of moderators and editors are associated with definitions; user groups of specification managers and specification developers are associated with specifications.
Assignment mappings
Assignment mappings are a way to create "super groups" of users for assigning steps in a workflow. They allow workflow standardization and let you create correlations between attributes such as functional areas, data systems, or specification types so that you can assign user groups to specific steps in workflow stages.
As mentioned in the Conditions section, the current implementation of Data Cookbook defines a standardized workflow that uses assignment mappings based on functional area. Direct experience and business requirements will dictate future revisions to this approach.
Named roles
Named roles allow you to define a "pool" of users who may be added to a workflow step when the step is initiated. These users are assigned by another defined "pool" of users who receive notification to make an assignment. If you are tasked with managing an assignment, named roles let you assign an individual user to a step in a workflow stage.
IU standard definition approval
Underlying assumptions
The stages of the IU standard definition approval workflow were created using the following assumptions:
- The fewer the variations that exist, the more understandable and maintainable the workflows will be.
- Data managers and data stewards should be involved as appropriate for reviewing, editing, and applying classification codes.
- Data managers should not be solely responsible for the creation of all definitions. Initial creation should take place as gaps are identified during the creation of specifications/reports by developers and functional experts.
- Quality assurance is necessary for good governance to ensure a solid body of consistent standardized information; however, QA should not adversely affect the workflow.
- All stages will have explicit steps that allow designated workflow administrative users to intervene and "unstick" the workflow as needed. This step will not be included in subsequent documentation.
Stages of standard definition approval
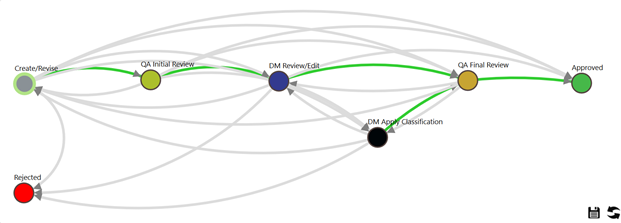
At IU, approval of a standard definition proceeds through the following stages; see below for a visual representation of these stages:
- Create/Revise
- QA Initial Review
- DM Review/Edit
- DM Apply Classification (optional)
- QA Final Review
- Approved
1. Create/Revise
During this stage, definitions are created and revised. This stage is made up of two primary steps, "Create/Revise Definition" and "Edit Draft as a Moderator".
a. Create/Revise Definition
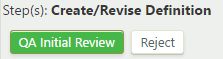
Access to the "Create/Revise Definition" step is available to definition editors associated with each functional area. These editors can create definitions and submit them for QA initial review, or they can reject definitions. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): Create/Revise Definition", click or :
b. Edit Draft as Moderator
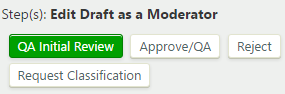
Access to the "Edit Draft as a Moderator" step is available to definition moderators; "moderator" is Data Cookbook's term for data managers or their delegates. Moderators fulfill an oversight role with regard to definition content, and in many cases also with regard to definition classification. Moderators have the ability not only to create definitions but also to submit them to multiple stages. In this stage, moderators can choose to approve definitions and submit them for final QA, if they believe the definitions are both accurate and complete. To take a transition action on the item, under "Step(s): Edit Draft as a Moderator", click , , , or :
2. QA Initial Review
During the QA initial review stage, definitions are checked for compliance with naming conventions and adherence to IU's Data Cookbook standards. Only administrators are able to edit a definition in the QA initial review stage, to ensure that QA is not being done on a moving target. In general, standards and formatting are overseen by the QA role, while the actual definition content and classification of the data are overseen by the moderator or data manager role. The EBI team within UITS is the service owner for Data Cookbook, and staff from the EBI team are currently responsible for QA. A definition that passes QA is submitted for DM review; if it does not pass QA, it will be returned to the previous stage for further revision.
The QA initial review stage is made up of the primary "QA Initial Review" step and an optional "QA Return for Revision" step.
a. QA Initial Review
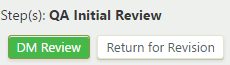
QA occurs during the "QA Initial Review" step. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): QA Initial Review", click or :
3. DM Review/Edit
In the DM review/edit stage, the moderator reviews, edits, or rewrites the definition. This stage is made up of two steps, the primary "DM Review/Edit" step and the optional "Revise Definition" step.
a. DM Review/Edit
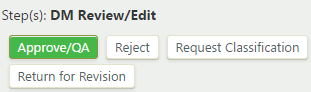
In the "DM Review/Edit" step, the moderators, who are the designated primary subject matter experts for the corresponding functional area, review the content of the definition. Moderators can choose to approve, modify, or rewrite the definition; return the definition to the initial stage for revision; or request that the classification be assigned. This step is at the heart of the data governance process. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): DM Review/Edit", click , , , or :
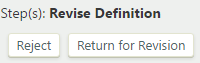
- Revise Definition: The optional "Revise Definition" step allows the initial definition creator or editor group to retrieve a definition from data manager review for further editing or revision. The creator or editor can retrieve the definition without intervention on the part of either the moderator or administrators. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): Revise Definition", click or :
4. DM Apply Classification (optional)
Apply classification is an optional stage where you can apply the security classification to the definition. In most cases, it is expected that the group responsible for the DM review/edit stage will supply the classification, but there are functional areas in which this will not be the case (for example, in student records, the Data Steward has delegated responsibility for the DM review/edit stage to UIRR, but the Student Data Management & Access group supplies the classification); for that reason, this step is optional. The original "Moderators by Functional Area" assignment mapping is used for the DM review/edit stage, while a new "Data Managers by Functional Area" assignment mapping is used for the apply classification stage.
The apply classification stage is made up of the primary "Apply Classification" step, and the optional "Request DM Revision" step.
a. Apply Classification
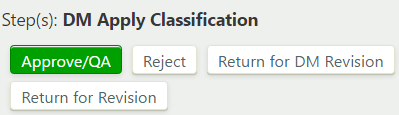
During the "Apply Classification" step, if there is a separation of duties for managing definition content and managing security, the classification is supplied. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): DM Apply Classification", click , , , or :
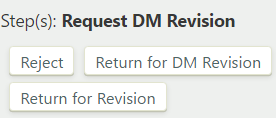
- Request DM Revision: In the "Request DM Revision" step, the data manager associated with the previous stage can retrieve a definition from the current stage for further editing. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): Request DM Revision", click , , or :
5. QA Final Review
During the QA final review stage, the definition gets a final check for completeness and adherence to IU's Data Cookbook standards. Only administrators are able to edit a definition in the QA final review stage, to ensure that QA is not being done on a moving target. The EBI team within UITS is the service owner for Data Cookbook, and staff from the EBI team are currently responsible for QA. A definition that passes final QA is approved and becomes the current official version.
The QA final review stage is made up of the primary "QA Final Approval" step and an optional "Request DM Revision" step.
a. QA Final Approval
Final QA occurs during the QA final approval step. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): QA Final Approval", click , , or :
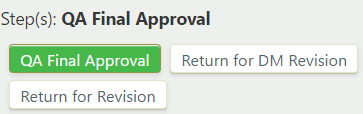
- Request DM Revision: In the "Request DM Revision" step, the data manager associated with the DM review/edit stage can retrieve a definition from the current stage for further editing. To take a transition action on the definition, under "Step(s): Request DM Revision", click , , or :

6. Approved
The approved stage is the final stage of the definition workflow. A definition that reaches this point has received approval for both content and format, and is the current official version for the IU Data Cookbook community. Any subsequent revision to an approved definition requires a new version of the definition to be created, and those new versions must go through the above workflow and be approved in their turn.
Rejected definitions
At various stages and steps in the workflow, appropriate users can choose to reject a definition for any reason (for example, duplication of definitions, discovery that the definition is not required).
This is document aolv in the Knowledge Base.
Last modified on 2023-09-29 16:34:05.